The DoC originated from the situation witnessed between 2014 and 2016 when the global oil market was confronted by one of the most severe downturns in its history. This had negative implications for the global economy. The Participating Countries that eventually formed OPEC+ recognized that the only way to deal with a challenge on this scale was to join hands and work together. The seed of this desire to cooperate gestated into the ‘170th OPEC Conference Decision’ of 28 September 2016, metamorphosing into the ‘171st OPEC Conference Decision’ of 30 November 2016 and blossoming into the historic ‘Declaration of Cooperation’ of 10 December 2016.
Originally effective for six months, the DoC’s voluntary adjustments in production have been extended many times and have become an indispensable tool in addressing market challenges and responding to developments that may impact the oil industry. Not only did this endeavor yield historical results, but it was also clear that there was a tremendous appetite among Participating Countries for further cooperation across a broad range of energy fronts. This includes knowledge exchange on long-term oil and energy perspectives, technological innovation aimed at enhancing efficiency, and cooperation to improve the environmental credentials of oil, among other areas.
This desire for further and broader cooperation has been institutionalized under the ‘Charter of Cooperation,’ which was signed by Participating Countries at the 6th OPEC and non-OPEC Ministerial Meeting on 2 July 2019. It is a high-level document to facilitate dialogue among Participating Countries aimed at promoting oil market stability and cooperation in technology and other areas for the benefit of oil producers, consumers, investors, and the global economy. It is a means of enabling the long-term use of oil as a key component in the evolving global energy mix while exploring efforts to improve the environmental and efficiency credentials of oil and strategies and technologies to advance the global oil industry.
The “Charter” promotes the principles of transparency, equity, and fairness. It also has, at its core, the concept of multi-stakeholders. This concept reflects OPEC’s desire to promote and participate in a wide and broad dialogue with all stakeholders in the energy industry, including oil producers, consumers, investors, analysts, and others. The Charter offers both a forum for dialogue among Participating Countries and between Participating Countries and other stakeholders.
Challenges Navigated 2017-2024
The challenges the oil market has faced over the last eight years have been multivarious and, at times, unprecedented. They include the severe oil market downturn of 2014-2016; technological innovation and disruption; geopolitical crises that have led to conflict in some regions; the COVID-19 pandemic and its subsequent impact on the market; macroeconomic uncertainty; historic levels of government stimulus packages; and a host of other factors and issues. When we reflect on the magnitude of all these changes, some of which occur only once in a century, we can appreciate the extent of the challenges the oil market faces. The DoC played an indispensable role in allowing the oil industry to survive all this turmoil and, indeed, thrive.
One of the most vivid demonstrations of this was how the DoC responded to the severe market disruptions caused by the apex of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020. During those days, market supply and demand fundamentals were continually out of sync. Global oil demand plummeted, some companies were filing for bankruptcy, and there was the prospect of massive job losses.
In the following graphs, the way oil market risk changes after the DOC is illustrated in the following figures:
Figure 1- Oil Market Risk Assessment 2007 M05- 2016 M12 (Before DoC)
Figure 2- Oil Market Risk Assessment 2017M01-2024M12(After DOC)
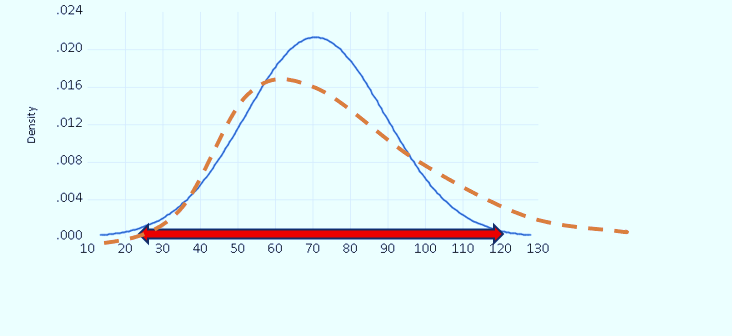
When comparing the aforementioned graphs, we observe that the standard deviation (or volatility) in the oil market decreased after the implementation of the DoC. This indicates that the DoC has contributed to relatively controlled oil market risk since 2017. A reduction in standard deviation suggests that the variability of returns has decreased, which is often associated with lower market risk.
In the second figure, the risk reduction is clearly illustrated. The dashed orange curve represents the market risk before the DoC, while the solid blue curve represents the market risk assessment after the DoC. The shift from the orange to the blue curve demonstrates a decrease in variance, which corresponds to a reduction in market risk.
Talks among major producers eventually culminated in three ‘Extraordinary’ meetings, two OPEC and non-OPEC Ministerial Meetings, and one from the G20, chaired by Saudi Arabia in 2020. At the 10th (Extraordinary) OPEC and non-OPEC Ministerial Meeting on 12 April 2020, OPEC+ decided on its largest-ever production adjustment in history and the longest in duration, as it was then valid until 30 April 2022. The clarity and assurance this provided the market was instrumental in allowing the industry to survive.
OPEC+ played a vital role in balancing the global oil market through voluntary production adjustments aimed at contributing to market stability. Over the subsequent five years, the DoC has modified production adjustments based on a thorough analysis of the world oil market. To accomplish this task, the DoC Ministerial Meetings are supported by the Joint Ministerial Monitoring Committee (JMMC), tasked with overseeing voluntary production adjustments, assessing market conditions, and proposing recommendations to the DoC Ministerial Meeting. Regular meetings of the JMMC have imbued the enterprise with flexibility and agility. Press releases stemming from OPEC and non-OPEC Ministerial Meetings (ONOM) usually give “the JMMC the authority to hold additional meetings, or to request an OPEC and non-OPEC Ministerial Meeting at any time to address market developments, whenever deemed necessary.”
OPEC and OPEC + have an important role to play, given the significance of Participating Countries as leading producers. This influence has helped them navigate market disruption caused by potential global political tensions that could impact the oil supply.
Looking Ahead: 2025
There is an array of uncertainties that the market will face in 2025. In the realm of geopolitics, the return of Donald Trump to the White House raises several potential issues. As the IMF has warned, trade tensions could lower investment and cause problems for supply chains around the world. Additionally, the Trump administration’s commitment to supporting production growth from the US oil and gas industry will have implications for non-DoC supply growth.
According to OPEC’s January edition of the Monthly Oil Market Report (MOMR), global economic growth is forecast to grow by 3.1% in 2025. This positive performance is underpinned by anticipated inflation normalization and corresponding adjustments to monetary policies in major economies. Global oil demand is forecast to grow by 1.4 mb/d. Non-DoC liquids supply is forecast to grow by 1.1 mb/d.
Whatever may come in 2025, the DoC has proven its credentials as an indispensable, volatility-fighting toolkit. As the OPEC+ Participating Countries have repeatedly emphasized, they remain unwavering in their commitment to achieve and sustain a stable oil market and to provide long-term guidance and transparency for the market, in line with the approach of being precautious, proactive, and pre-emptive.
Given the potential uncertainty in the oil market in 2025, OPEC+ will play a more prominent role in stabilizing the market. For this reason, OPEC+ will need to be flexible in its approach. However, what is certain is that despite the pressure of sanctions on some Members, the existence and continuity of cooperation among OPEC and OPEC+ participating countries in 2025 is vital for maintaining relative stability in the oil market.
It is important to note the impact of narratives on the energy industry. The OPEC Secretariat, deploying the same diligence it has throughout the DoC process, will continue to use all the necessary tools to proactively engage with the media through its ongoing communications strategy. Such engagement will render the DoC even more effective in its market stabilization efforts.
I would like to categorize oil market uncertainty as the following:
- Global Policy Risks such as US tariffs;
- Non-OPEC supply;
- Role of narratives;
- FED, ECB, and BOJ Monetary and financial policies;
- Possible shifting of global demand; and
- The escalation of geopolitical tension.
Remarkable Achievement
The world has undergone remarkable changes and seen historic events in the last eight years. These have had major implications for the oil market. The DoC Participating Countries deserve an enormous amount of praise for their deft handling of these many challenges. Undoubtedly, this formula for success, honed by experience, will continue in the years ahead.
There are many uncertainties for the oil market in 2025, including the interplay of US energy policies, global geopolitical shifts, and monetary decisions. OPEC and OPEC+ will continue to be vital players in 2025. While challenges like fluctuating demand and future energy pathways will require careful navigation, OPEC+ efforts will be essential in maintaining market stability.
Afshin Javan
Energy Economist


Your Comment